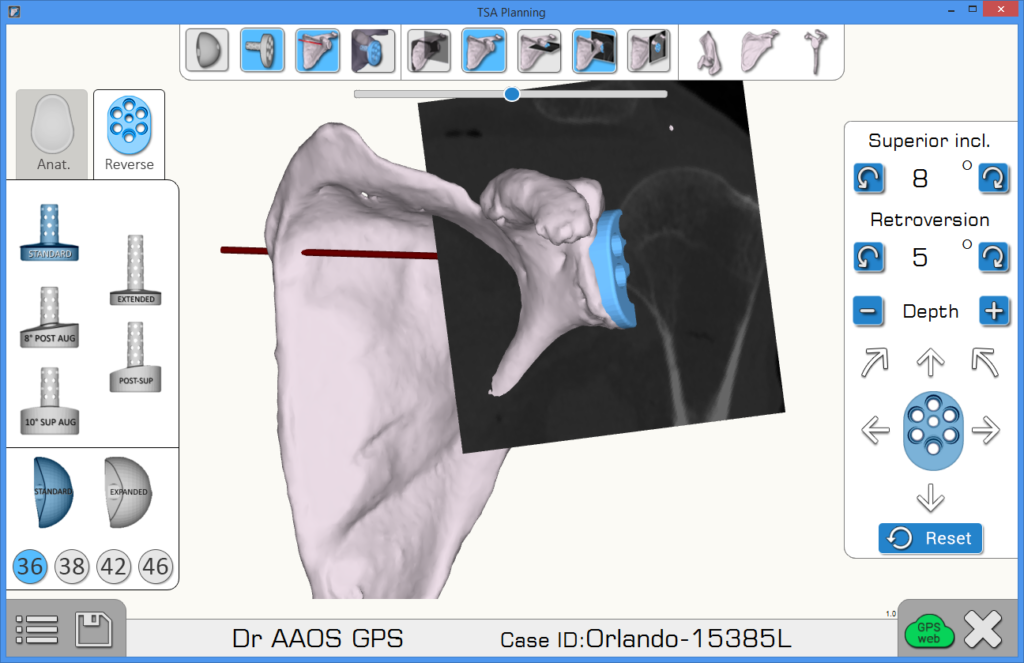
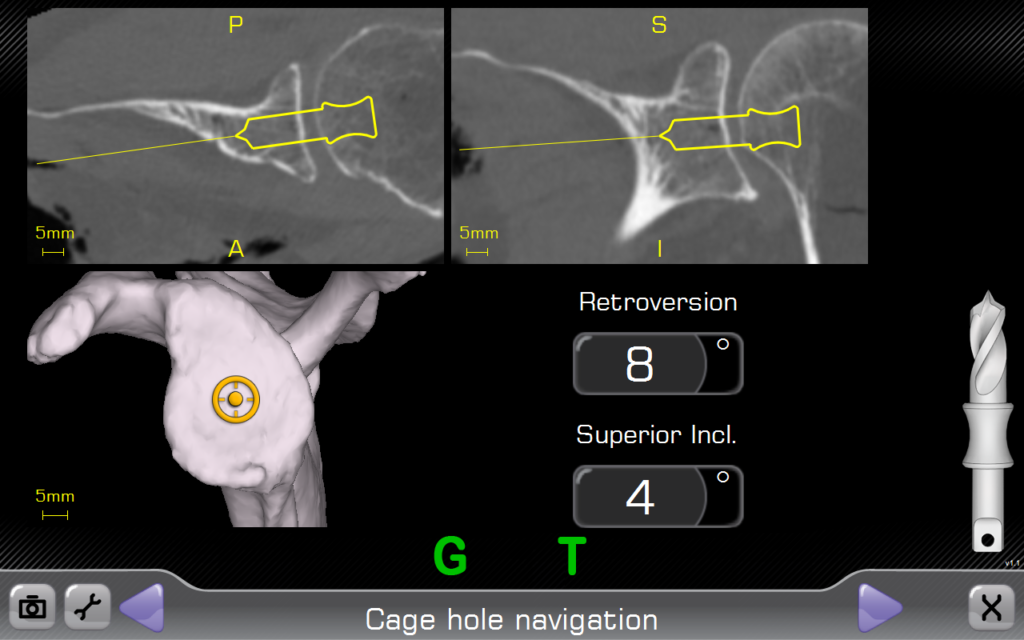
Stai pianificando ma non navigando?
Un migliore
caso eseguito
- Flessibilità intraoperatoria
- Visibilità della volta glenoidea in tempo reale
- Precisione migliorata1,12
- Migliore fissazione13,14
- Tempo neutrale dopo i casi iniziali15,16
- Nessun costo di capitale
chirurghi guidati entro 2 mm dal posizionamento dell’impianto e 2° di versione/inclinazione rispetto al loro piano1

azienda ortopedica per lanciare a livello globale la navigazione per la spalla

Le spalle Equinoxe sono navigate utilizzando ExactechGPS®
ARTICOLI DI GIORNALE CON REVISIONE PARI
ARTICOLI DI GIORNALE CON REVISIONE PARI

SITI CLINICI
PIÙ DI
PAZIENTI
78%
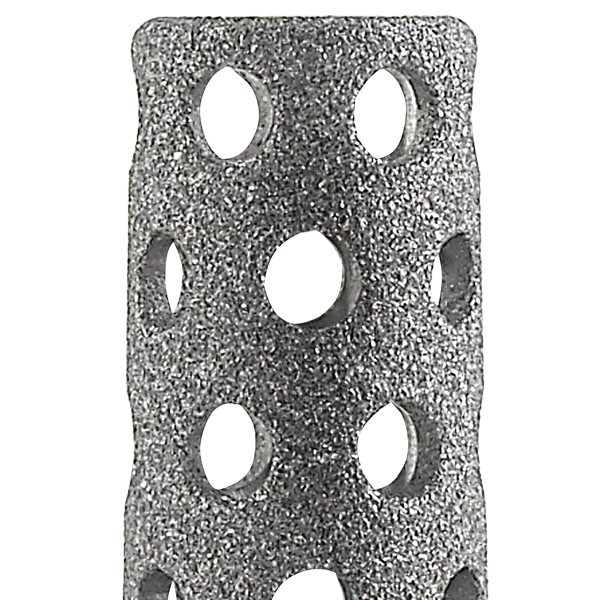
Stelo della piattaforma6
aTSA conserve di aumento del cuneo8
89%
più osso di una glenoide standard
51%
più osso di un disegno a gradini
Inversione
0.5%
instabilità5
@4Y
4X
riduzione delle linee radiotrasparenti della glenoide TSA
(gabbia contro tutto-poli)9
3X
MIGLIORAMENTO
nella rotazione esterna post-operatoria7
SOLUZIONI PER 100%
delle procedure di artroplastica della spalla, da semplici a impegnative

ANNUALE COMPOSTO
TASSO DI CRESCITA
PRINCIPALE
lanci di prodotti all’anno
°
AL MERCATO
con sistema di ricostruzione omerale progettato biomeccanicamente
15+Y
DI USO CLINICOE
Fin dall’inizio e
ancora innovando

PRIMO AL MERCATO
con sistema di ricostruzione omerale progettato biomeccanicamente
DI USO CLINICO
Sin dall’inizio
e ancora innovando

PRIMO
per offrire aumenti inversi

PRIMO
per offrire aumenti inversi

Cerchi maggiori informazioni o vuoi farti contattare da un Product Manager o un rappresentante di vendita?
Forza di Equinoxe in numeri Risorse
- Greene, A. et al. Navigated vs. non-navigated results of a CT based computer assisted shoulder arthroplasty system in 30 cadavers. Presented at ISTA 2018.*
- Simovitch, R. et al. Effect of tuberosity healing on clinical outcomes in elderly patients treated with a reverse shoulder arthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma 33(2), e39-e45. 2019.
- Mollon, B. et al. Impact of scapular notching on clinical outcomes after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of 476 shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 26(7), 1253–1261. 2017.
- King, J. et al. How common are acromial and scapular spine fractures after reverse shoulder arthroplasty? Bone Joint J 2019;101-B:627–634.
- Friedman, RJ. et al. Comparison of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty outcomes with and without subscapularis repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Apr;26(4):662-668. 2017.
- Crosby, L. et al. Conversion to reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with and without humeral stem retention: the role of a convertible platform stem. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 3 maggio 2017;99(9):736-742.
- Friedman RJ. et al. Comparison of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty outcomes with and without subscapularis repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Apr. 2017;26(4):662-668.
- Kersten, AD. et al. Posterior augmented glenoid designs preserve more bone in biconcave glenoids. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Lug. 2015;24(7):1135-41. AND Roche, C. et al. Biomechanical impact of posterior glenoid wear on anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty. Bulletin for the Hospital for Joint Diseases. 71(2):S5-11. 2013.
- Friedman, RJ. et al. Clinical and radiographic comparison of a hybrid cage glenoid to a cemented polyethylene glenoid in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty. Articolo in stampa. J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2019) -, 1-9.
- Stroud, N. et al. Initial glenoid fixation using two different reverse shoulder designs with an equivalent center of rotation in a low-density and high-density bone substitute. J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2013) 22, 1573-1579. AND Stroud, N. et al. Reverse shoulder glenoid loosening: an evaluation of the initial fixation associated with six different reverse shoulder designs. Bulletin of the Hospital for Joint Diseases 2013;71(Suppl 2):S12-7.*
- Simovitch, R. et al. Quantifying success after total shoulder arthroplasty: the minimal clinically important difference. J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2018) 27, 298–305.
- Nashikkar P., et al. Role of intraoperative navigation in the fixation of the glenoid component in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a clinical case-control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Set. 2019;28(9):1685-1691.
- Nashikkar P., et al. Computer navigation re-creates planned glenoid placement and reduces correction variability in total shoulder arthroplasty: an in vivo case-control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 25 luglio 2019. Articolo in stampa.
- Roche C., et al. Impact of screw length and screw quantity on rTSA glenoid fixation for two different sizes of glenoid baseplates. JSES Open Access (JSESOA-D-19-00048R1).*
- Greene A., et al. Clinical Use of a Computer Assisted Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty System: An Analysis of 574 Cases. Presented at CAOS 2019.
- Greene A., et al. Clinical Use of a Computer Assisted Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty System: An Analysis of 1702 Cases. Presented at CAOS 2019.
*I risultati dei test in vitro (banco) potrebbero non essere necessariamente indicativi delle prestazioni cliniche.
References for JSES April 2020 ads:
- Greene A. et al. Navigated vs. non-navigated results of a CT based computer assisted shoulder arthroplasty system in 30 cadavers. Presented at ISTA 2018.*
- Nashikkar P., et al. Role of intraoperative navigation in the fixation of the glenoid component in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a clinical case-control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Set. 2019;28(9):1685-1691.
- Nashikkar P., et al. Computer navigation re-creates planned glenoid placement and reduces correction variability in total shoulder arthroplasty: an in vivo case-control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 25 luglio 2019. Articolo in stampa.
- Roche C., et al. Impact of screw length and screw quantity on rTSA glenoid fixation for two different sizes of glenoid baseplates. JSES Open Access (JSESOA-D-19-00048R1).*
- Greene A., et al. Clinical Use of a Computer Assisted Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty System: An Analysis of 574 Cases. Presented at CAOS 2019.
- Greene A., et al. Clinical Use of a Computer Assisted Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty System: An Analysis of 1702 Cases. Presented at CAOS 2019.
*I risultati dei test in vitro (banco) potrebbero non essere necessariamente indicativi delle prestazioni cliniche.